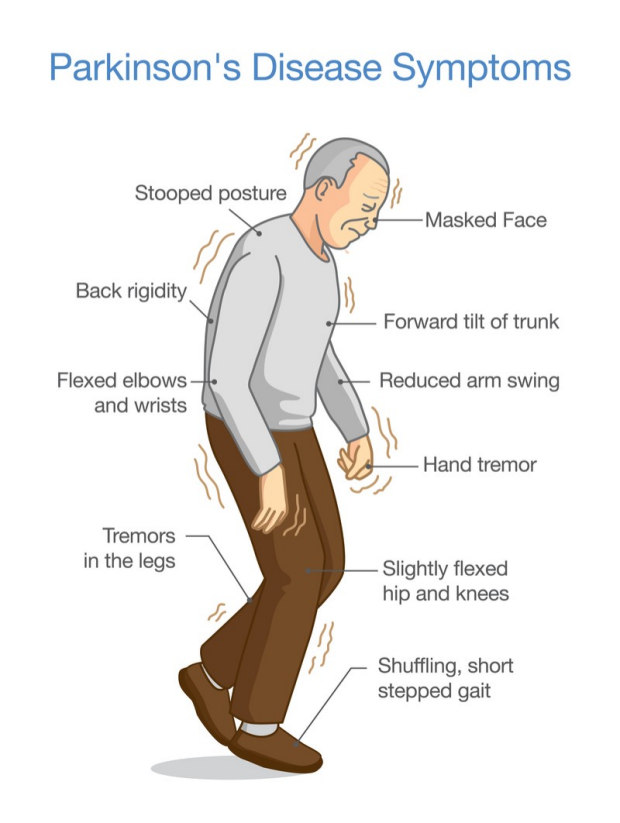
- Parkinson’s disease is a chronic, progressive disorder of the nervous system characterized by the cardinal features of rigidity, akinesia, bradykinesia, tremor, and postural instability.
- In this article, we’ll be discussing how to identify the signs of Parkinson’s disease, the diagnostic process, and the possible treatments or solutions.
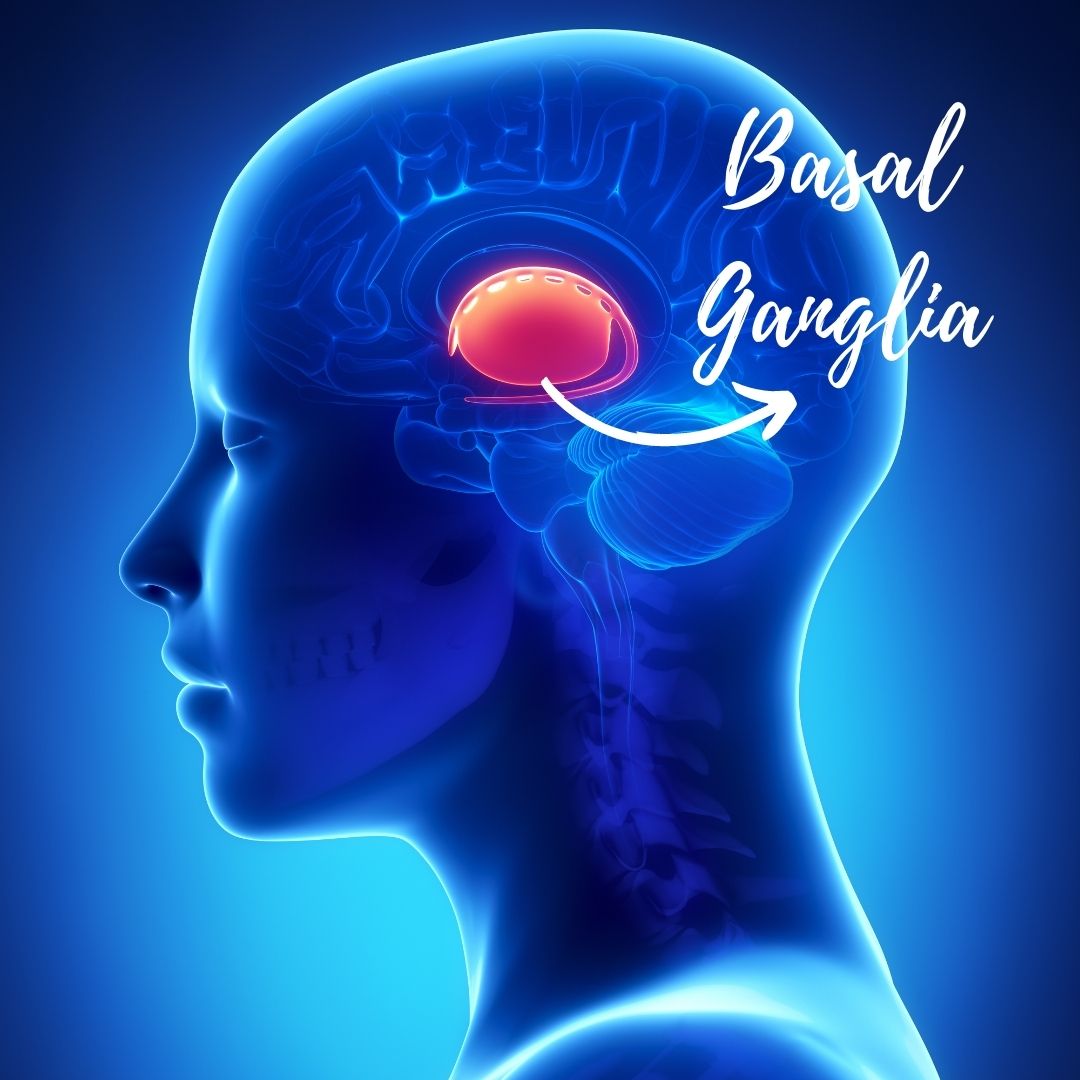
- The term parkinsonism is used to refer to a group of disorders that produce abnormalities of basal ganglia function.
- Parkinson’s disease or primary parkinsonism is the most common cause affecting about 78% of the patients. Secondary parkinsonism results from any different cause. Parkinsonism plus syndromes imply the symptoms of multiple system degeneration.
- According to recent statistics, over 10 million people in the world have Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that occurs when neurons in the brain break down. When these nerve cells die, it reduces dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that sends messages from one nerve cell to another.
- Low dopamine levels are correlated with abnormal brain activity. Parkinson’s is usually the first symptom of this, which can lead to tremors.