Knee Osteoarthritis (Knee Joint Pain)
Knee Osteoarthritis (Knee Joint Pain): Stages, Causes & Treatment
OA –Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the articular cartilage and the subchondral bone. Joints commonly affected with this condition may include hands, feet and spine and the large weight-bearing joints such as the hip and knee. Arthritis is prevalent generally in older adults, though in younger adults too and most common in women than in men. This is a slowly developing process complaining of pain which worsens with time. In addition to these, obesity, joint injuries or any trauma’s become the predisposing factors for OA.
Characteristics:
Reduced movement secondary to the stiffness of the joint and pain, atrophy of local muscles surrounding the joint, ligamental laxity, muscular weakness and instability of the joint, loss of muscle strength contributes to functional limitation of the affected limb which is characterized by reduced or loss of ROM.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Pain and stiffness in performing activities like running, walking, kneeling and bending which even worsens throughout the day.
- Inflammation of the joint with tenderness.
- Joint effusion
- Synovitis
- Crepitus and
- Deformity
As OA is diagnosed into 4 stages (acute, mild, moderate and severe), symptoms may not be noticed in the early stages.
A complete physical examination along with personal and family medical histories should be done.
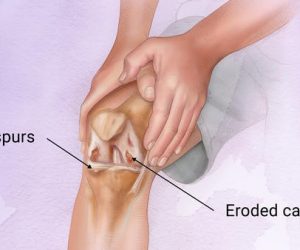
Knee clinical and radiographic examinations include X-rays which show osteophyte formation and narrowing of joint space.
MRI Scans (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) to find out the stages of OA differentiating with cyst formations in the joint and subchondral sclerosis.
Joint aspiration may also be performed which involves the removal of synovial fluid from the joint with a needle and sent for further laboratory testing which indicates an increase of leukocyte count from 500 cells mm- to 2000 cells mm- in severe graded OA.
Treatment:
Treatment recommendations help an individual to get rid of the pain and swelling meanwhile maintaining the daily activities and improving the quality of life.
Physical Therapy:
Includes treatments such as
Cold and Heat therapy: This can help decrease swelling and increase blood flow (circulation) promoting range and relief.
Electrotherapy:
This includes treatment with electrotherapeutic modalities like Interferential Therapy, Ultrasound, Transcutaneous Electrical Muscle Stimulation which helps to relieve pain. These therapies are directly applied to the skin.
Laser Therapy:
It is a non-invasive treatment that has an analgesic as well as the modulatory effect on microcirculation.
Hydrotherapy:
Also referred to as aquatic therapy which uses water to decrease the symptoms of OA and helps to facilitate motion while performing gentle exercises underwater.
Manual therapy:
Manual therapy along with electrotherapy has proven to be effective in improving joint mobility and pain when combined with advanced exercises. Active treatment (exercises) included strengthening exercises and flexibility exercises which can be done at home to strengthen the weaker muscles around the joint and increase flexibility, ROM, and strength.
Precautions for OA Knee:
- Limited or reduced stair climbing and prolonged standing
- Avoid cross-sitting
- Avoid using Indian toilets
- Control of body weight.
- Regular exercise.
Check out these links for relevant information: Sports
physiotherapy
