Meniscal Tear
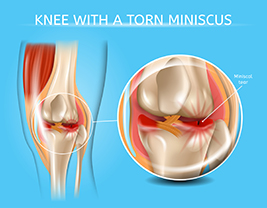
Meniscal tear or meniscal injuries are present in different populaces, and it can be due to traumatic, intense traumatic presentations happening more frequently at a younger age during sports competition and practice. A traumatic meniscal tear is seen with the history of sudden onset of the joint line pain which is related to an adequate knee injury. Meniscal tear is common in knee injuries. A torn meniscus happens since of injury caused by intense bending or hyper-flexing of the knee joint.
These meniscal tear injuries can be seen in all age groups due to several conditions like degeneration and trauma. Most commonly meniscal tears are seen in younger people due to trauma. When a shear force happens between the femur and tibia the typical twisting constraints on a weight-loaded flexed knee lead to meniscal damage. Meniscal tear incidence may be as high as 6 per 1000 population with a 2.5 to 4 times male predominance. The injury occurs more than 20-29 years. Over the past decade, meniscal root tears have gotten to be more recognized as a critical source of pain and inability.
The knee menisci are fibrocartilaginous structures that sit within the knee joint, deepening the tibiofemoral articulation. Menisci transfer the axial load from the femur to the tibia additionally acts as shock absorbers, lubricants and stabilizes the knee during flexion, extension, and minimal rotation, it plays an important role in keeping up the knee joint stability and congruency, force dissemination, and proprioception and decreases the improvement of osteoarthritis. It also plays an important role in synovial fluid dynamic circulation menisci are vascularized only via the periphery and the root attachment gets its nutrition through blood vessels; the inner portions are avascular must rely on the diffusion of synovial fluid the location of a meniscal lesion, along with age and health of the patient influences the options available after injury because of the capacity of the meniscus to heal.
Causes of meniscal tear:
- Older individuals regularly get meniscus tears since their menisci get to be fragile and less adaptable with age. But for teenagers as a rule happen since of damage. This might happen when;
- Lifting heavy objects
- Making sudden changes in direction
- Sports like soccer, tennis, basketball, football, racquetball
- Taking a direct hit to the knee while playing a contact sport such as football, hockey, or rugby, where the knee may be forced to twist or turn awkwardly
- Falling in a way that puts a lot of strain on the knee, can happen in sports like skiing or snowboarding.
Symptoms of Meniscal Tear:
- Joint line tenderness
- Pain within the center or side of the knee, particularly when bending the knee or squatting.
- Swelling& stiffness in the knee that gets worse over the first 2 or 3 days after the injury occurs.
- Loss of range of motion
- A feeling of locking and instability
- Difficulty to move the knee
- Slipping or popping sensation
Meniscal tears are commonly diagnosed clinically using special tests like Thessaly’s test (specificity 97.7%), Mc Murray’s test (specificity 95%), and applies test (specificity 90%).
Thessaly’s test has symptomatic accuracy when it is performed at 20 degrees of knee flexion. A history of locking of the knee joint, pain with passive terminal knee extension joint line tenderness, and positive special tests when all these signs were present in patients for detections of meniscal tears. Quiet history combined with special tests can create a demonstrative precision of 90%, slightly prevalent to the diagnostic precision of MRI alone exercise has been appeared to progress knee function and diminish pain.
Treatment for Meniscal Tear:
Taking anti-inflammatory drugs like acetaminophen, and ibuprofen can help to relieve pain and swelling in the affected area.
Physiotherapy:
It can help to strengthen your leg muscles, stabilize the knee and get your knee back to its full ROM & Flexibility.
Short-term and long-term follow-up studies had shown that exercise therapy improves the function and activities in patients with meniscal tears. There’s the possibility to cure by conservative treatment if patients get diagnosed prior by different tests done by the clinical practices. In patients, meniscal tear showed similar results between orthoscopic meniscectomy and physical treatment be that as it may the physical therapy group had a higher rate of improvement cross over to surgery.
Conservative Treatment for meniscal tears includes active exercises that focus to increase the range of motion and muscle strength, reducing pain, improve balance and flexibility.
Most treatment of torn meniscus may include observation and physical therapy with muscle strengthening to stabilize the knee joint.
Reported outcomes of surgery and conservative treatment are similar. Hence there’s a require for extra research into nonoperative alternate treatment strategies for treating the symptoms of meniscal tears as there’s constrained back that nonoperative elective treatments are effective. When the conservative measures are ineffective treatments may include surgery to repair or remove the damaged cartilage.
The physical treatment program included in stages the criteria for progressing from one stage to the next, including pain, strength, range motion knee effusion, and functional mobility, supervised exercise treatment appeared positive impacts over surgery in progressing thigh muscle strength within the short term.
Brain mulligan developed mulligan manual techniques used to reduce pain, and sensory and motor deficits and restore the movements. It includes the technique of sustained passive accessory glides with an active motion or mobilizations with movement (MWM). The manual therapy of the mulligan squeeze technique is used to treat joint line pain and reduced range of motion in meniscal tears.
Mulligan mobilization together with exercise convention leads to a decrease in pain, functional advancement additionally progresses ROM and muscle strength. Conventional therapy along with the mulligan squeeze technique is more effective in patients with a meniscal tear
Precautions:
- Get regular exercise including strength training for your leg muscles. Strong leg muscles offer assistance to stabilize and ensure the knee.
- Always warm-up and extend appropriately sometime recently playing sports or engaging in any strenuous activities.
- Give your muscles plenty of time to rest & recover between activities.
- Get the correct footwear for sports.
- Use proper techniques in sport.
- If you have previously had a knee injury, a brace or wrap can give added support to your knee.
Check out these links for relevant information: Sports physiotherapy

Progressive Care Physiotherapy
Progressive Care Physiotherapy Management is the best service in the physiotherapy industry. It is known for providing the best service and cutting-edge technology to help speed up recovery, while also being able to offer various treatment options that are tailored to your specific needs.
For More details call us on 9618906780
