Possible Effects of Head Injuries & It’s Immediate Treatment
Head Injuries and Treatment
Most head injuries are due to direct violence resulting from RTA and industrial accidents. Two distinct mechanisms are recognized by which injury to the brain tissue occurs.
- A traumatizing object strikes the head.it results in cross injury, bullet injury, stab injury, etc. The skull remains intact but the damage to brain tissue occurs. When the fracture occurs bony fragments may be depressed with laceration of underlying bone tissue.
- The moving head strikes to a fixed object which results in compression, distortion of brain tissue at the site of grow.it may results in contusion or hemorrhage .then occurs fracture at the site of the blow. The common source of head injury is from rotational or linear acceleration forces.
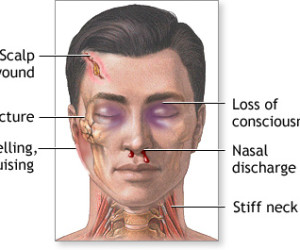
Fracture skull:
Fracture skull may occur without damage to brain substance and damage of the brain may occur without the fractured skull. linear fracture is of little consequence. compound linear fracture may give rise to infection.
Depressed fracture ranges from without scalp laceration to bony depression with scalp and brain laceration
Concussion
It is a condition of widespread paralysis of brain function and recovers spontaneously, it is also known as mild TBI. No gross change in organic substance occurs. Mi. minor cases are reversible whereas severe cases are followed by demyelination. The patient becomes unconscious to few seconds to several weeks, recovers with impairment of higher functions like post-traumatic amnesia and retrograde amnesia
Contusion
It is a more or less diffuse disturbance to the brain and characterized by edema & capillary hemorrhage. The patient is unconscious in severe cases depth of coma increases and pt dies of medullary paralysis within a few hours.less sever cases recovers passes into a state of mental confusion like delirium, confusion, disorientation.
Laceration
Visible breath in the continuity of brain substance.
Intracranial Haemorrhage:
Extradural hemorrhage:
The blood accumulated and clot which is encapsulated. depending upon the size and site it may compress the underlying brain substance so gradually pt may develop the sign and symptom.in case of neurological deficit surgical evaluation is considered.
Subdural hemorrhage:
It occurs at any age caused by trauma the precipitating factors are alcoholism, hemorrhagic dis, anticoagulant therapy. blood slowly accumulated in subdural space.there is a gradual onset of headache, drowsiness,confusion., ptosis may be present.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage:
Occurs due to rupture of an intracranial aneurysm, angioma, AV malformation. Hypertention may be the precipitating factor.symptoms may be an irritable headache, meningeal sign, cervical rigidity, kerning sign, papilloedema, pyrexia, areflexia, and focal symptom present.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage:
Occurs in middle age, males are more prone than females.positive family history. the hemorrhage due to HTN or atherosclerosis.the hemorrhage occurs in the neighborhood of the internal capsule, cerebellum or pons. Sudden onset of symptoms by physical mental exertion, headache, vomiting, loss of consciousness, convulsion may be present.
Evaluation
Glassgow coma scale: as per GCS mild 13 to 15, moderate 9 to 12, sever less than 8
Check respiration rate, rhythm, depth, pattern, oxygen saturation
Check CVS pulse, depth, BP, temp.
Auscultate for air entry, breath sound, added sound, heart sound.
Check the posture, position, reflexes, movt
Post Traumatic Physiotherapy:
It varies from a pt with consciousness to pt without consciousness again from an unconscious pt with spontaneous breathing to conscious pt with a ventilator.
Turning every 2hrly will prevent pressure sore and respiratory complication
RPM should be given twice daily from proximal to the distal joint to maintain JROM, prevent adaptive shortening, remembrance of the pattern.
Conscious Patient With Spontaneously Breathing Patient:
Breathing exercise: diaphragmatic breathing, deep diaphragmatic breathing, effective huffing coughing.In manual techniques such as percussion, vibration, shaking help in loosening, dislodging the secretion.
Patient suction is used. modified postural drainage is indicated in case of lung collapse.pt cant put in a head-down position which may aggravate the swelling of the brain.
Unconscious Patient With Ventilator
A back squeezing technique is used to access the removal of secretions and find out the lung segment having secretion.
Chest physiotherapy, postural drainage can be helpful
Reduction of movement in functional activities.
Check out these links for relevant information: Neurological physiotherapy
For more details contact
us on 📞9618906780
